Spatial Ecology of Coyotes along a Suburban-to-Rural Gradient
Abstract
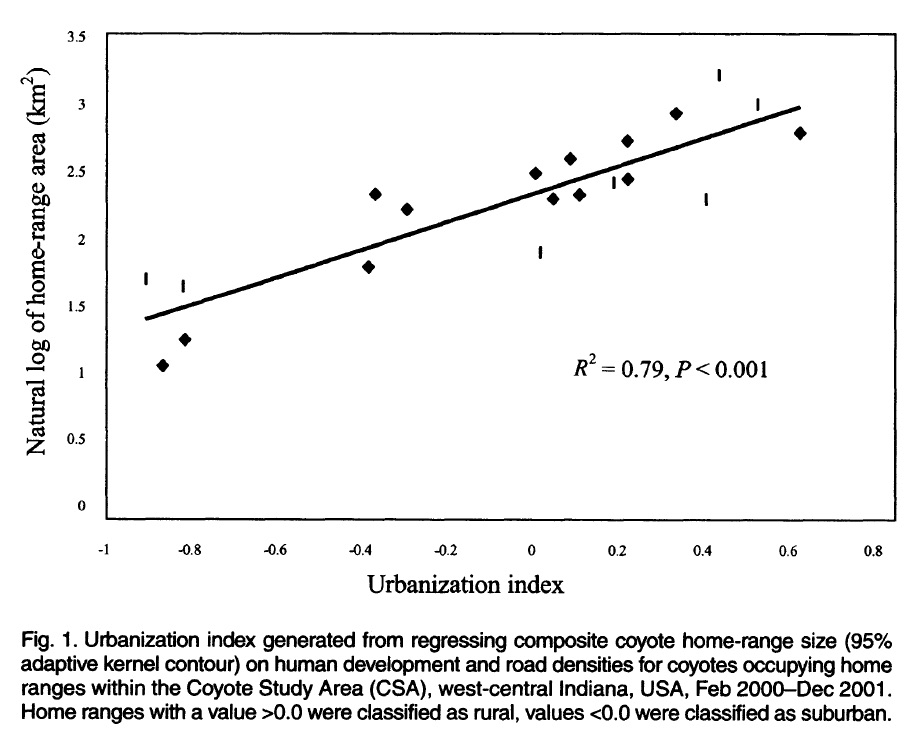
Abstract: Coyotes (Canis latrans) are now ubiquitous throughout most of the eastern United States; however, little information exists on how they are able to exploit and thrive in fragmented landscapes. We investigated home ranges, movements, and scale-dependent resource selection of coyotes along a gradient (suburban/exurban/rural) of anthropogenic disturbance. Home-range sizes varied along a suburban-to-rural gradient and were inversely correlated to urbanization (R2 = 0.79, P< 0.001). Habitat composition and coyote use of 95% (home range) and 50% (core area) contours were nonrandom. Coyotes used corridor habitat extensively and avoided urban and crop-field habitats. Forested habitat was used extensively for diurnal cover. Rural coyotes traveled greater distances at faster rates than did suburban/exurban coyotes. Diel activity patterns were similar along the gradient, suggesting that coyotes responded similarly to differing levels and types of human activity. Coyotes appeared to assess habitat quality at the landscape scale and exploited small, distinct resource patches present in developed landscapes. We believe that the availability of foraging habitat and travel corridors is critical to movement of coyotes in areas of high human activity.”
